Install Oracle express
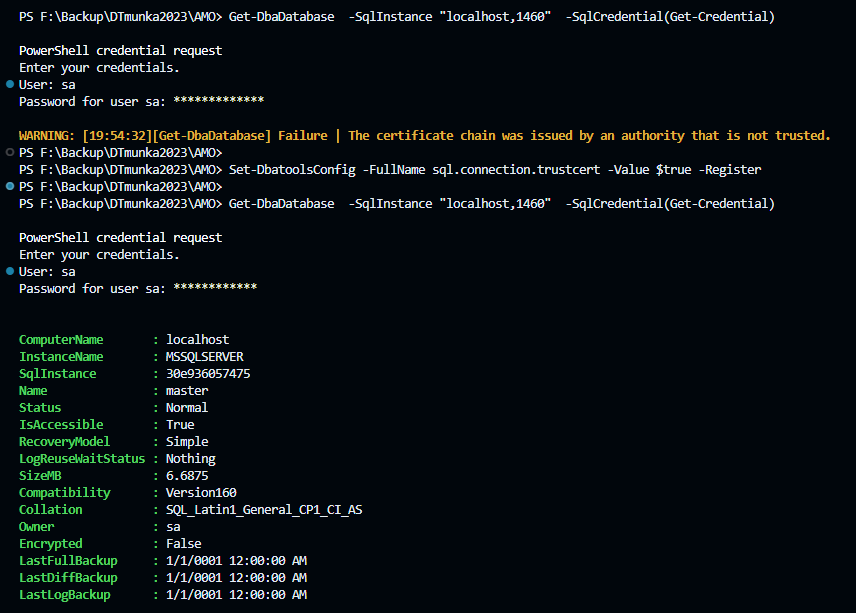
docker command in windows powershell (WSL installed):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
docker login container-registry.oracle.com docker container create -it --name oracletest -p 1521:1521 -e ORACLE_PWD=alma123 container-registry.oracle.com/database/express:latest docker start oracletest # chek it later docker exec oracletest env |
download oracle sqldeveloper Windows 64-bit with JDK 11 included:
https://www.oracle.com/database/sqldeveloper/technologies/download/